Hash map based on multi-level array. More...
#include <cds/container/impl/feldman_hashmap.h>

Public Types | |
| typedef GC | gc |
| Garbage collector. | |
| typedef Key | key_type |
| Key type. | |
| typedef T | mapped_type |
| Mapped type. | |
| typedef std::pair< key_type const, mapped_type > | value_type |
| Key-value pair to be stored in the map. | |
| typedef Traits | traits |
| Map traits. | |
| typedef traits::hash | hasher |
Hash functor, see feldman_hashmap::traits::hash. | |
| typedef maker::hash_type | hash_type |
Hash type deduced from hasher return type. | |
| typedef base_class::hash_comparator | hash_comparator |
hash compare functor based on Traits::compare and Traits::less | |
| typedef traits::item_counter | item_counter |
| Item counter type. | |
| typedef traits::allocator | allocator |
| Element allocator. | |
| typedef traits::node_allocator | node_allocator |
| Array node allocator. | |
| typedef traits::memory_model | memory_model |
| Memory model. | |
| typedef traits::back_off | back_off |
| Backoff strategy. | |
| typedef traits::stat | stat |
| Internal statistics type. | |
| typedef feldman_hashmap::level_statistics | level_statistics |
| Level statistics. | |
| typedef gc::template guarded_ptr< value_type > | guarded_ptr |
| Guarded pointer. | |
| typedef implementation_defined | iterator |
| bidirectional iterator type | |
| typedef implementation_defined | const_iterator |
| bidirectional const iterator type | |
| typedef implementation_defined | reverse_iterator |
| bidirectional reverse iterator type | |
| typedef implementation_defined | const_reverse_iterator |
| bidirectional reverse const iterator type | |
Public Member Functions | |
| FeldmanHashMap (size_t head_bits=8, size_t array_bits=4) | |
| Creates empty map. More... | |
| ~FeldmanHashMap () | |
| Destructs the map and frees all data. | |
| template<typename K > | |
| bool | insert (K &&key) |
| Inserts new element with key and default value. More... | |
| template<typename K , typename V > | |
| bool | insert (K &&key, V &&val) |
| Inserts new element. More... | |
| template<typename K , typename Func > | |
| bool | insert_with (K &&key, Func func) |
| Inserts new element and initialize it by a functor. More... | |
| template<typename K , typename... Args> | |
| bool | emplace (K &&key, Args &&... args) |
For key key inserts data of type value_type created in-place from std::forward<Args>(args)... More... | |
| template<typename K , typename Func > | |
| std::pair< bool, bool > | update (K &&key, Func func, bool bInsert=true) |
Updates data by key. More... | |
| template<typename K > | |
| bool | erase (K const &key) |
Delete key from the map. More... | |
| template<typename K , typename Func > | |
| bool | erase (K const &key, Func f) |
Delete key from the map. More... | |
| bool | erase_at (iterator const &iter) |
Deletes the element pointed by iterator iter. More... | |
| template<typename K > | |
| guarded_ptr | extract (K const &key) |
Extracts the item from the map with specified key. More... | |
| template<typename K > | |
| bool | contains (K const &key) |
Checks whether the map contains key. More... | |
| template<typename K , typename Func > | |
| bool | find (K const &key, Func f) |
Find the key key. More... | |
| template<typename K > | |
| guarded_ptr | get (K const &key) |
Finds the key key and return the item found. More... | |
| void | clear () |
| Clears the map (non-atomic) More... | |
| bool | empty () const |
| Checks if the map is empty. More... | |
| size_t | size () const |
| Returns item count in the map. | |
| stat const & | statistics () const |
| Returns const reference to internal statistics. | |
| size_t | head_size () const |
| Returns the size of head node. | |
| size_t | array_node_size () const |
| Returns the size of the array node. | |
| void | get_level_statistics (std::vector< feldman_hashmap::level_statistics > &stat) const |
Collects tree level statistics into stat. More... | |
Thread-safe iterators | |
| iterator | begin () |
| Returns an iterator to the beginning of the map. More... | |
| const_iterator | begin () const |
| Returns an const iterator to the beginning of the map. | |
| const_iterator | cbegin () |
| Returns an const iterator to the beginning of the map. | |
| iterator | end () |
| Returns an iterator to the element following the last element of the map. This element acts as a placeholder; attempting to access it results in undefined behavior. | |
| const_iterator | end () const |
| Returns a const iterator to the element following the last element of the map. This element acts as a placeholder; attempting to access it results in undefined behavior. | |
| const_iterator | cend () |
| Returns a const iterator to the element following the last element of the map. This element acts as a placeholder; attempting to access it results in undefined behavior. | |
| reverse_iterator | rbegin () |
| Returns a reverse iterator to the first element of the reversed map. | |
| const_reverse_iterator | rbegin () const |
| Returns a const reverse iterator to the first element of the reversed map. | |
| const_reverse_iterator | crbegin () |
| Returns a const reverse iterator to the first element of the reversed map. | |
| reverse_iterator | rend () |
| Returns a reverse iterator to the element following the last element of the reversed map. More... | |
| const_reverse_iterator | rend () const |
| Returns a const reverse iterator to the element following the last element of the reversed map. More... | |
| const_reverse_iterator | crend () |
| Returns a const reverse iterator to the element following the last element of the reversed map. More... | |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static constexpr size_t const | c_nHazardPtrCount = base_class::c_nHazardPtrCount |
| Count of hazard pointers required. | |
| static constexpr size_t const | c_hash_size = base_class::c_hash_size |
The size of hash_type in bytes, see feldman_hashmap::traits::hash_size for explanation. | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Protected Types inherited from cds::intrusive::FeldmanHashSet< GC, std::pair< Key const, T >, Traits > Protected Types inherited from cds::intrusive::FeldmanHashSet< GC, std::pair< Key const, T >, Traits > | |
| typedef GC | gc |
| Garbage collector. | |
| typedef std::pair< Key const, T > | value_type |
| type of value stored in the set | |
| typedef Traits | traits |
Traits template parameter, see feldman_hashset::traits. | |
| typedef traits::hash_accessor | hash_accessor |
| Hash accessor functor. | |
| typedef base_class::hash_type | hash_type |
Hash type deduced from hash_accessor return type. | |
| typedef traits::disposer | disposer |
| data node disposer | |
| typedef base_class::hash_comparator | hash_comparator |
hash compare functor based on traits::compare and traits::less options | |
| typedef traits::item_counter | item_counter |
| Item counter type. | |
| typedef traits::node_allocator | node_allocator |
| Array node allocator. | |
| typedef traits::memory_model | memory_model |
| Memory model. | |
| typedef traits::back_off | back_off |
| Backoff strategy. | |
| typedef traits::stat | stat |
| Internal statistics type. | |
| typedef gc::template guarded_ptr< value_type > | guarded_ptr |
| Guarded pointer. | |
| typedef feldman_hashset::level_statistics | level_statistics |
| Level statistics. | |
| typedef implementation_defined | iterator |
| bidirectional iterator type | |
| typedef implementation_defined | const_iterator |
| bidirectional const iterator type | |
| typedef implementation_defined | reverse_iterator |
| bidirectional reverse iterator type | |
| typedef implementation_defined | const_reverse_iterator |
| bidirectional reverse const iterator type | |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from cds::intrusive::FeldmanHashSet< GC, std::pair< Key const, T >, Traits > Protected Member Functions inherited from cds::intrusive::FeldmanHashSet< GC, std::pair< Key const, T >, Traits > | |
| FeldmanHashSet (size_t head_bits=8, size_t array_bits=4) | |
| Creates empty set. More... | |
| ~FeldmanHashSet () | |
| Destructs the set and frees all data. | |
| bool | insert (value_type &val) |
| Inserts new node. More... | |
| bool | insert (value_type &val, Func f) |
| Inserts new node. More... | |
| std::pair< bool, bool > | update (value_type &val, bool bInsert=true) |
| Updates the node. More... | |
| bool | unlink (value_type const &val) |
Unlinks the item val from the set. More... | |
| bool | erase (hash_type const &hash) |
| Deletes the item from the set. More... | |
| bool | erase (hash_type const &hash, Func f) |
| Deletes the item from the set. More... | |
| bool | erase_at (iterator const &iter) |
Deletes the item pointed by iterator iter. More... | |
| guarded_ptr | extract (hash_type const &hash) |
Extracts the item with specified hash. More... | |
| bool | find (hash_type const &hash, Func f) |
Finds an item by it's hash. More... | |
| bool | contains (hash_type const &hash) |
Checks whether the set contains hash. More... | |
| guarded_ptr | get (hash_type const &hash) |
Finds an item by it's hash and returns the item found. More... | |
| void | clear () |
| Clears the set (non-atomic) More... | |
| bool | empty () const |
| Checks if the set is empty. More... | |
| size_t | size () const |
| Returns item count in the set. | |
| stat const & | statistics () const |
| Returns const reference to internal statistics. | |
| void | get_level_statistics (std::vector< feldman_hashset::level_statistics > &stat) const |
Collects tree level statistics into stat. More... | |
| iterator | begin () |
| Returns an iterator to the beginning of the set. More... | |
| const_iterator | begin () const |
| Returns an const iterator to the beginning of the set. | |
| const_iterator | cbegin () |
| Returns an const iterator to the beginning of the set. | |
| iterator | end () |
| Returns an iterator to the element following the last element of the set. This element acts as a placeholder; attempting to access it results in undefined behavior. | |
| const_iterator | end () const |
| Returns a const iterator to the element following the last element of the set. This element acts as a placeholder; attempting to access it results in undefined behavior. | |
| const_iterator | cend () |
| Returns a const iterator to the element following the last element of the set. This element acts as a placeholder; attempting to access it results in undefined behavior. | |
| reverse_iterator | rbegin () |
| Returns a reverse iterator to the first element of the reversed set. | |
| const_reverse_iterator | rbegin () const |
| Returns a const reverse iterator to the first element of the reversed set. | |
| const_reverse_iterator | crbegin () |
| Returns a const reverse iterator to the first element of the reversed set. | |
| reverse_iterator | rend () |
| Returns a reverse iterator to the element following the last element of the reversed set. More... | |
| const_reverse_iterator | rend () const |
| Returns a const reverse iterator to the element following the last element of the reversed set. More... | |
| const_reverse_iterator | crend () |
| Returns a const reverse iterator to the element following the last element of the reversed set. More... | |
 Static Protected Attributes inherited from cds::intrusive::FeldmanHashSet< GC, std::pair< Key const, T >, Traits > Static Protected Attributes inherited from cds::intrusive::FeldmanHashSet< GC, std::pair< Key const, T >, Traits > | |
| static constexpr size_t const | c_nHazardPtrCount |
| Count of hazard pointers required. | |
| static constexpr size_t const | c_hash_size |
The size of hash_type in bytes, see feldman_hashset::traits::hash_size for explanation. | |
Detailed Description
template<class GC, typename Key, typename T, class Traits = feldman_hashmap::traits>
class cds::container::FeldmanHashMap< GC, Key, T, Traits >
Hash map based on multi-level array.
- [2013] Steven Feldman, Pierre LaBorde, Damian Dechev "Concurrent Multi-level Arrays: Wait-free Extensible Hash Maps"
[From the paper] The hardest problem encountered while developing a parallel hash map is how to perform a global resize, the process of redistributing the elements in a hash map that occurs when adding new buckets. The negative impact of blocking synchronization is multiplied during a global resize, because all threads will be forced to wait on the thread that is performing the involved process of resizing the hash map and redistributing the elements. FeldmanHashSet implementation avoids global resizes through new array allocation. By allowing concurrent expansion this structure is free from the overhead of an explicit resize, which facilitates concurrent operations.
The presented design includes dynamic hashing, the use of sub-arrays within the hash map data structure; which, in combination with perfect hashing, means that each element has a unique final, as well as current, position. It is important to note that the perfect hash function required by our hash map is trivial to realize as any hash function that permutes the bits of the key is suitable. This is possible because of our approach to the hash function; we require that it produces hash values that are equal in size to that of the key. We know that if we expand the hash map a fixed number of times there can be no collision as duplicate keys are not provided for in the standard semantics of a hash map.
FeldmanHashMap is a multi-level array which has an internal structure similar to a tree:
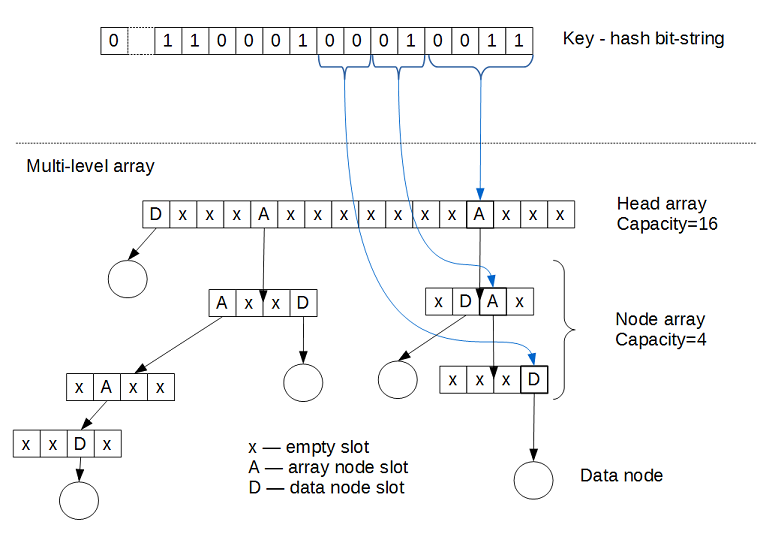
The multi-level array differs from a tree in that each position on the tree could hold an array of nodes or a single node. A position that holds a single node is a dataNode which holds the hash value of a key and the value that is associated with that key; it is a simple struct holding two variables. A dataNode in the multi-level array could be marked. A markedDataNode refers to a pointer to a dataNode that has been bitmarked at the least significant bit (LSB) of the pointer to the node. This signifies that this dataNode is contended. An expansion must occur at this node; any thread that sees this markedDataNode will try to replace it with an arrayNode; which is a position that holds an array of nodes. The pointer to an arrayNode is differentiated from that of a pointer to a dataNode by a bitmark on the second-least significant bit.
FeldmanHashMap multi-level array is similar to a tree in that we keep a pointer to the root, which is a memory array called head. The length of the head memory array is unique, whereas every other arrayNode has a uniform length; a normal arrayNode has a fixed power-of-two length equal to the binary logarithm of a variable called arrayLength. The maximum depth of the tree, maxDepth, is the maximum number of pointers that must be followed to reach any node. We define currentDepth as the number of memory arrays that we need to traverse to reach the arrayNode on which we need to operate; this is initially one, because of head.
That approach to the structure of the hash map uses an extensible hashing scheme; the hash value is treated as a bit string and rehash incrementally.
- Note
- Two important things you should keep in mind when you're using
FeldmanHashMap:- all keys is converted to fixed-size bit-string by hash functor provided. You can use variable-length keys, for example,
std::stringas a key forFeldmanHashMap, but real key in the map will be fixed-size hash values of your keys. For the strings you may use well-known hashing algorithms like SHA1, SHA2, MurmurHash, CityHash or its successor FarmHash and so on, which converts variable-length strings to fixed-length bit-strings, and such hash values will be the keys inFeldmanHashMap. If your key is fixed-sized the hash functor is optional, seefeldman_hashmap::traits::hashfor explanation and examples. FeldmanHashMapuses a perfect hashing. It means that if two different keys, for example, of typestd::string, have identical hash then you cannot insert both that keys in the map.FeldmanHashMapdoes not maintain the key, it maintains its fixed-size hash value.
- all keys is converted to fixed-size bit-string by hash functor provided. You can use variable-length keys, for example,
The map supports bidirectional thread-safe iterators.
Template parameters:
GC- safe memory reclamation schema. Can begc::HP,gc::DHPor one of RCU typeKey- a key type to be stored in the mapT- a value type to be stored in the mapTraits- type traits, the structure based onfeldman_hashmap::traitsor result offeldman_hashmap::make_traitsmetafunction.
There are several specializations of FeldmanHashMap for each GC. You should include:
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ FeldmanHashMap()
|
inline |
Creates empty map.
- Parameters
-
head_bits - 2head_bits specifies the size of head array, minimum is 4. array_bits - 2array_bits specifies the size of array node, minimum is 2.
Equation for head_bits and array_bits:
where N is multi-level array depth.
Member Function Documentation
◆ begin()
|
inline |
Returns an iterator to the beginning of the map.
The map supports thread-safe iterators: you may iterate over the map in multi-threaded environment. It is guaranteed that the iterators will remain valid even if another thread deletes the node the iterator points to: Hazard Pointer embedded into the iterator object protects the node from physical reclamation.
- Note
- Since the iterator object contains hazard pointer that is a thread-local resource, the iterator should not be passed to another thread.
Each iterator object supports the common interface:
- dereference operators: value_type [const] * operator ->() noexceptvalue_type [const] & operator *() noexcept
- pre-increment and pre-decrement. Post-operators is not supported
- equality operators
==and!=. Iterators are equal iff they point to the same cell of the same array node. Note that for two iteratorsit1andit2, the conditonit1 == it2does not entail&(*it1) == &(*it2) - helper member function
release()that clears internal hazard pointer. Afterrelease()the iterator points tonullptrbut it still remain valid: further iterating is possible.
During iteration you may safely erase any item from the set; erase_at() function call doesn't invalidate any iterator. If some iterator points to the item to be erased, that item is not deleted immediately but only after that iterator will be advanced forward or backward.
- Note
- It is possible the item can be iterated more that once, for example, if an iterator points to the item in array node that is being splitted.
◆ clear()
|
inline |
Clears the map (non-atomic)
The function unlink all data node from the map. The function is not atomic but is thread-safe. After clear() the map may not be empty because another threads may insert items.
◆ contains()
|
inline |
Checks whether the map contains key.
The function searches the item by its hash that is equal to hash( key_type( key )) and returns true if it is found, or false otherwise.
◆ crend()
|
inline |
Returns a const reverse iterator to the element following the last element of the reversed map.
It corresponds to the element preceding the first element of the non-reversed container. This element acts as a placeholder, attempting to access it results in undefined behavior.
◆ emplace()
|
inline |
For key key inserts data of type value_type created in-place from std::forward<Args>(args)...
Returns true if inserting successful, false otherwise.
◆ empty()
|
inline |
Checks if the map is empty.
Emptiness is checked by item counting: if item count is zero then the map is empty. Thus, the correct item counting feature is an important part of the map implementation.
◆ erase() [1/2]
|
inline |
Delete key from the map.
key_type must be constructible from value of type K. The function deletes the element with hash value equal to hash( key_type( key ))
Return true if key is found and deleted, false otherwise.
◆ erase() [2/2]
|
inline |
Delete key from the map.
The function searches an item with hash value equal to hash( key_type( key )), calls f functor and deletes the item. If key is not found, the functor is not called.
The functor Func interface:
where item is the element found.
key_type must be constructible from value of type K.
Return true if key is found and deleted, false otherwise
◆ erase_at()
|
inline |
Deletes the element pointed by iterator iter.
Returns true if the operation is successful, false otherwise.
The function does not invalidate the iterator, it remains valid and can be used for further traversing.
◆ extract()
|
inline |
Extracts the item from the map with specified key.
The function searches an item with key equal to hash( key_type( key )) in the map, unlinks it from the map, and returns a guarded pointer to the item found. If key is not found the function returns an empty guarded pointer.
The item extracted is freed automatically by garbage collector GC when returned guarded_ptr object will be destroyed or released.
- Note
- Each
guarded_ptrobject uses the GC's guard that can be limited resource.
Usage:
◆ find()
|
inline |
Find the key key.
The function searches the item by its hash that is equal to hash( key_type( key )) and calls the functor f for item found. The interface of Func functor is:
where item is the item found.
The functor may change item.second.
The function returns true if key is found, false otherwise.
◆ get()
|
inline |
Finds the key key and return the item found.
The function searches the item with a hash equal to hash( key_type( key )) and returns a guarded pointer to the item found. If key is not found the function returns an empty guarded pointer.
It is safe when a concurrent thread erases the item returned as guarded_ptr. In this case the item will be freed later by garbage collector GC automatically when guarded_ptr object will be destroyed or released.
- Note
- Each
guarded_ptrobject uses one GC's guard which can be limited resource.
Usage:
◆ get_level_statistics()
|
inline |
Collects tree level statistics into stat.
The function traverses the set and collects statistics for each level of the tree into feldman_hashset::level_statistics struct. The element of stat[i] represents statistics for level i, level 0 is head array. The function is thread-safe and may be called in multi-threaded environment.
Result can be useful for estimating efficiency of hash functor you use.
◆ insert() [1/2]
|
inline |
Inserts new element with key and default value.
The function creates an element with key and default value, and then inserts the node created into the map.
Preconditions:
- The
key_typeshould be constructible from a value of typeK. In trivial case,Kis equal tokey_type. - The
mapped_typeshould be default-constructible.
Returns true if inserting successful, false otherwise.
◆ insert() [2/2]
|
inline |
Inserts new element.
The function creates a node with copy of val value and then inserts the node created into the map.
Preconditions:
- The
key_typeshould be constructible fromkeyof typeK. - The
value_typeshould be constructible fromvalof typeV.
Returns true if val is inserted into the map, false otherwise.
◆ insert_with()
|
inline |
Inserts new element and initialize it by a functor.
This function inserts new element with key key and if inserting is successful then it calls func functor with signature
The argument item of user-defined functor func is the reference to the map's item inserted:
item.firstis a const reference to item's key that cannot be changed.item.secondis a reference to item's value that may be changed.
key_type should be constructible from value of type K.
The function allows to split creating of new item into two part:
- create item from
key; - insert new item into the map;
- if inserting is successful, initialize the value of item by calling
funcfunctor
This can be useful if complete initialization of object of value_type is heavyweight and it is preferable that the initialization should be completed only if inserting is successful.
◆ rend() [1/2]
|
inline |
Returns a reverse iterator to the element following the last element of the reversed map.
It corresponds to the element preceding the first element of the non-reversed container. This element acts as a placeholder, attempting to access it results in undefined behavior.
◆ rend() [2/2]
|
inline |
Returns a const reverse iterator to the element following the last element of the reversed map.
It corresponds to the element preceding the first element of the non-reversed container. This element acts as a placeholder, attempting to access it results in undefined behavior.
◆ update()
|
inline |
Updates data by key.
The operation performs inserting or replacing the element with lock-free manner.
If the key not found in the map, then the new item created from key will be inserted into the map iff bInsert is true (note that in this case the key_type should be constructible from type K). Otherwise, if key is found, it is replaced with a new item created from key. The functor Func signature:
where:
item- item of the mapold- old item of the map, ifnullptr- the new item was inserted
The functor may change any fields of the item.second.
Returns std::pair<bool, bool> where first is true if operation is successful, second is true if new item has been added or false if key already exists.
- Warning
- See insert item troubleshooting
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- cds/container/impl/feldman_hashmap.h